Printed From:
Printed From:
Lovenox is a low molecular weight heparin [LMWH] indicated for1:
Prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in abdominal surgery, hip replacement surgery, knee replacement surgery, or medical patients with severely restricted mobility during acute illness
Inpatient treatment of acute DVT with or without pulmonary embolism.
Outpatient treatment of acute DVT without pulmonary embolism
Prophylaxis of ischemic complications of unstable angina and non–Q-wave myocardial infarction [MI]
Treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction [STEMI] managed medically or with subsequent percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI]
Surgical patients
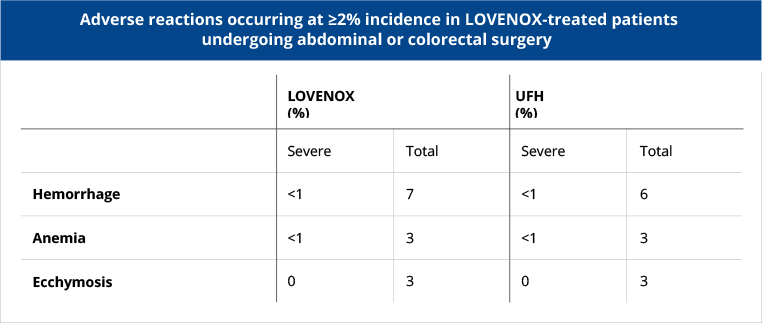
In patients undergoing abdominal surgery who are at risk for thromboembolic complications, Lovenox is indicated for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE).
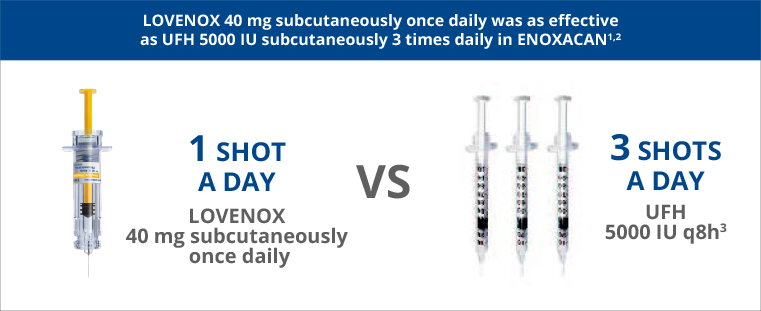
In patients with cancer undergoing surgical resection, Lovenox 40 mg subcutaneous once daily was as effective as unfractionated heparin (UFH) 5000 IU subcutaneous 3 times daily.1
In this study, 1115 patients undergoing elective cancer surgery of the GI, urological, or gynecological tract, were treated with Lovenox 40 mg subcutaneously qd or heparin 5000 U TID. Patients ages ranged from 32 to 97 years (mean 67 years). DVT/PE/death occurred in 10.1% (95% CI: 8 to 13) of Lovenox-treated patients and 11.3% (95% CI: 9 to 14) of heparin-treated patients.
Adverse Events: Major bleeding episodes occurred in 4% and 3% of patients in the Lovenox and heparin arms, respectively.1
Inpatient and Outpatient Settings
Lovenox provides equivalent risk reduction for1:
Inpatient setting
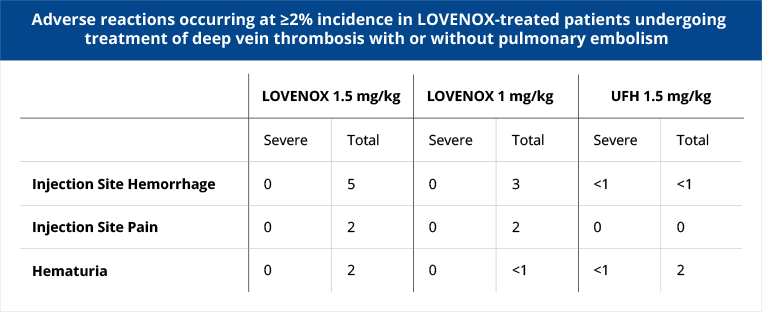
Inpatient treatment with Lovenox vs standard heparin provided equivalent risk reduction for recurrent venous TE.
A randomized, controlled, partially blinded equivalence trial was conducted in the inpatient setting. Patients up to 155 kg with acute lower extremity deep vein thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism were treated with either Lovenox 1.5 mg/kg daily subcutaneously or Lovenox 1.0 mg/kg subcutaneous bid or heparin. A total of 900 patients ranging in age from 18 to 92 years (mean 60.7 years) were included.
Adverse Events: Incidence of major hemorrhagic complications was 1.7%, 1.3% and 2.1% in patients receiving Lovenox 1.5 mg/kg/day, Lovenox 1.0 mg/kg/12 hr, and UFH, respectively.
NS= not significant N=900
At baseline, 32% had DVT with PE.
Outpatient setting
In the outpatient setting, to reduce the risk of recurrent venous TE in treatment of acute DVT, Lovenox when given with warfarin sodium was equivalent to inpatient treatment with standard heparin.
In the outpatient setting, patients with acute proximal DVT were randomized to either Lovenox 1 mg/kg subcutaneous q12h or heparin. Patients in the heparin group received inpatient treatment; patients in the Lovenox group were permitted to go home on therapy. Mean time spent in the hospital after randomization for Lovenox patients was 1.1 ± 2.9 days.
Adverse Events: For the two studies combined, 2% of patients in each treatment arm experienced major bleeding episodes. Incidence of major hemorrhagic complications was 2.0% with Lovenox and 1.2% with UFH.1,5
NS= not significant N=500
95% CI for the treatment difference was -5.6 to 2.7.
In Acute STEMI Patients
Lovenox saved lives and reduced reinfarction vs UFH in acute STEMI patients.1
ExTRACT-TIMI 25—landmark study in >20,000 acute STEMI patients6,7
ExTRACT-TIMI 25 was a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, parallel-group, multinational, active-controlled clinical trial comparing Lovenox with UFH in acute STEMI patients.6,7
Significant net clinical benefits
Based upon these calculations from trial results, Lovenox had an estimated 21 fewer of the combined endpoint of death or MI per 1,000 STEMI patients vs UFH, with 7 additional major bleeds.8The rates of major hemorrhage at 30 days were 2.1% in the Lovenox group and 1.4% in the UFH group. Rates of intracranial hemorrhage at 30 days were 0.8% and 0.7% in the Lovenox and UFH groups, respectively.
UA/NSTEMI
Lovenox is indicated for the prophylaxis of ischemic complications of unstable angina (UA) and non–Q-wave MI when concurrently administered with aspirin.
In UA/NSTEMI patients, Lovenox when administered concomitantly with aspirin, significantly reduced the incidence of the combined endpoint of death, MI, or recurrent angina vs UFH.
Patients with recent unstable angina or non-Q-wave MI were treated with either Lovenox 1 mg/kg subcutaneous q12h or heparin. A total of 3,107 patients ranging in age from 25 to 94 years (median age 64 years) were treated. All patients also received aspirin 100 mg to 325 mg per day. The combined incidence of the triple endpoint of death, MI, or recurrent angina was lower with Lovenox vs heparin therapy at 14 days and sustained up to 30 days, after initiation of treatment.
Adverse Events: Major bleeding episodes occurred in 1% of patients in each treatment group.

View dosing guidelines for each indication.
GET THE INFORMATIONLearn about Enoxaparin Sodium Injection—the authorized generic that is identical to Lovenox.
SEE THE DETAILS
Warning: spinal/epidural hematomas
Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in
patients who are anticoagulated with low molecular weight heparins (LMWH) or heparinoids
and are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis.